(An Autonomous Body Recognized by Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India)
Competency based placement focussed Education | Training | Research | Consultancy
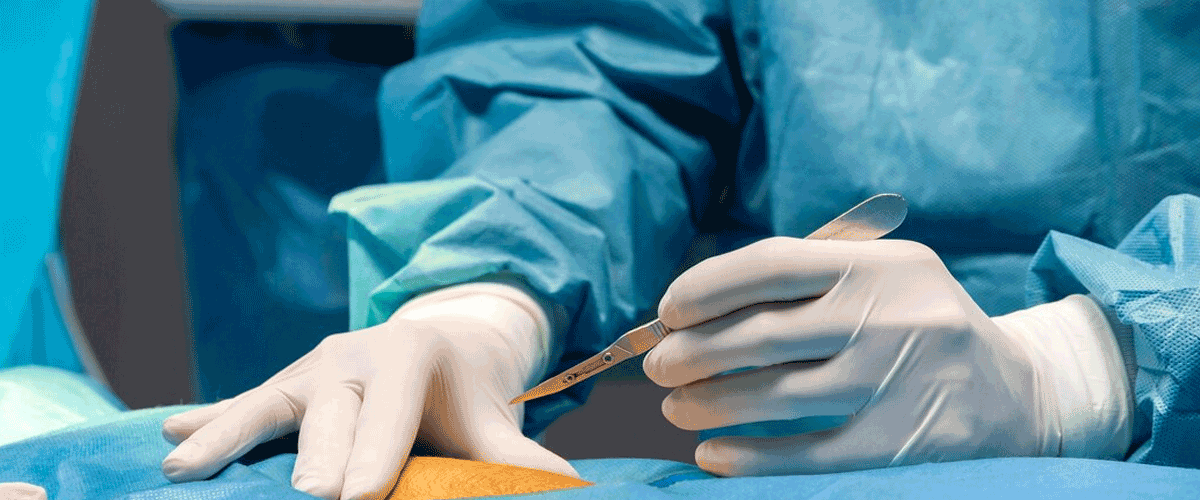
Safer Gallbladder Surgery Now Possible for High-Risk Patients
Gallbladder removal, particularly through laparoscopic cholecystectomy, is usually a safe procedure. However, elderly patients and those with conditions such as heart, lung or kidney disease, diabetes, or metabolic syndrome face higher chances of complications. Advances in minimally invasive surgery, perioperative care, and multidisciplinary teamwork have now made these surgeries safer.
Experts note that early surgical intervention is often the best choice if no major contraindications exist, supported by an experienced surgical team. In some cases, conservative management with antibiotics and supportive care is preferred until the patient stabilises for elective surgery.
For critically ill patients, procedures like percutaneous gallbladder drainage (PT-GBD) or endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage (EUS-GBD) are lifesaving, while endoscopic transpapillary drainage (ET-GBD) is used selectively. Once the patient recovers, cholecystectomy can be performed safely after six weeks. Emerging tools such as robotic systems and AI-based risk prediction promise even better outcomes for high-risk patients in the future.
25-08-2025
📰 Recent News
- Dr Lal PathLabs Unveils Sovaaka: A New-Age Diagnostic Experience Centre in Gurugram
- Finger-Prick Blood Test Could Revolutionize Alzheimer’s Research
- Practo Expands Care Navigation Platform to the U.S., Building on Global Momentum
- CDC Reduces Recommended Childhood Vaccines from 17 to 11
- Shared Genetics Explain Why Mental Health Disorders Often Overlap
- 2026 Emerges as Turning Point for Non-Invasive Drug Delivery in Pharma and MedTech
- Technology Integration Transforms Medical Transportation for Chronic Care in India
- Technology-Driven Innovations Reshape India’s Eye Care Ecosystem
- Xortx Underscores Genetic Evidence for Xanthine Oxidase Targeting and Announces Board Update
- Strengthening Regional Healthcare: A Priority for India’s Future
